What Is ALS?
First identified in 1869 by
Jean-Martin Charcot (a French neurologist), it only started getting
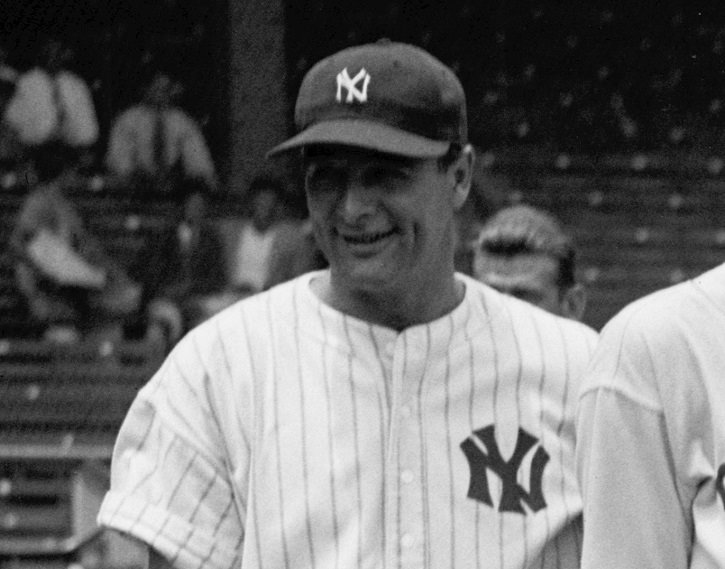
attention in 1939 because of Lou Gehrig, as it ended his career as one
of the most famous baseball players ever. ALS is also known as Motor
Neuron Disease (MND) or “Charcot Disease” and in the U.S. it is commonly
referred to as “Lou Gehrig Disease”.

ALS stands for “Amyotrophic Lateral
Sclerosis”. It is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that
degenerates nerve cells in the brain and the spinal cord, leading to
death. As degenerate and neurons die, the brain’s ability to control the
muscles is lost. Patients in the later stages of the disease often
become paralyzed.
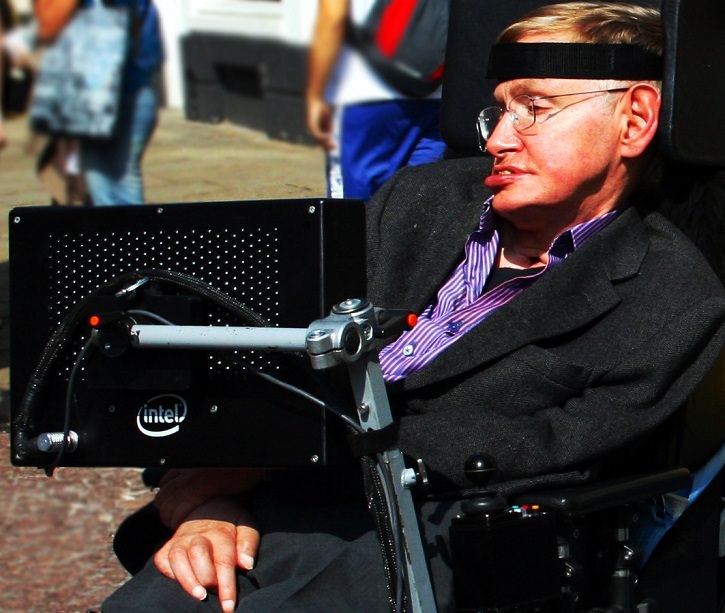

Stephen Hawking has been living with ALS for 50 years
On average, the time from onset to
death is 39 months. Only about 4% of patients survive longer than 10
years (though rare cases have survived for 50 years). The most common
reason of death is due to respiratory failure and happens within three
to five years from when symptoms appear.
|
|
Symptoms:
About 75% of people who contract ALS
experience "limb onset": The first symptoms are in the arms or legs.
When the arms are affected, patients find it difficult to do simple
tasks like turning a key. Patients with affected legs have trouble
walking and even suffer from a dragging-leg.

The other 25% of cases are "bulbar
onset": The symptoms are difficulty speaking or swallowing, with speech
becoming slurred & nasal and difficulty swallowing or loss of tongue
mobility.
In few cases, patients experience
"respiratory onset": The muscles that support breathing are affected
first, making it difficult to breath.
|
|
Causes:
While there is no conclusive cause
for ALS other than genetic tendency, potential causes include head
trauma, military service, drug abuse, and participation in contact
sports. Recently, research has suggested a link between ALS and food
contaminated by blue-green algae. ALS is NOT contagious.
 |
|
Diagnosis:
At this time, there is no test can
provide a definite diagnosis of ALS. The diagnosis of ALS is based on
symptoms and signs observed in the patient, combined with a series of
tests. As well as a regular follow-up to make sure that symptoms are not
getting worse.
|
|
Treatment:
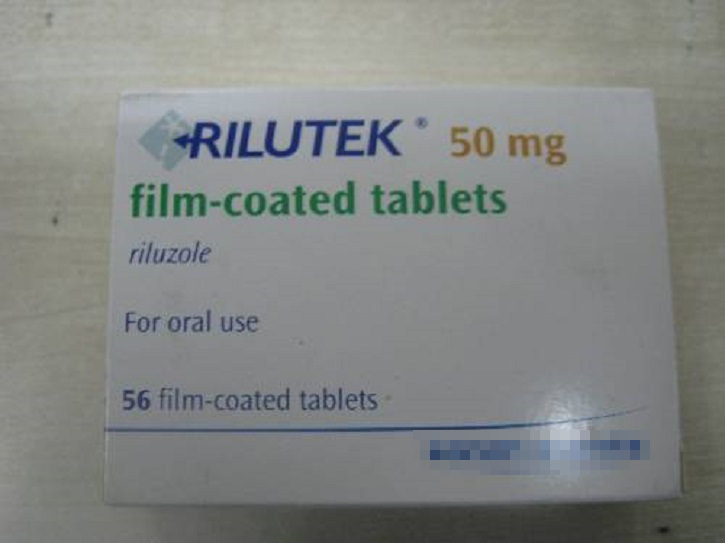
The only treatment that has been
found to lengthen survival by several months is Riluzole, which also
extends the time before patients need breathing support. However, it
does not reverse the damage already done to the brain, and can damage
the liver (roughly 10% of users).
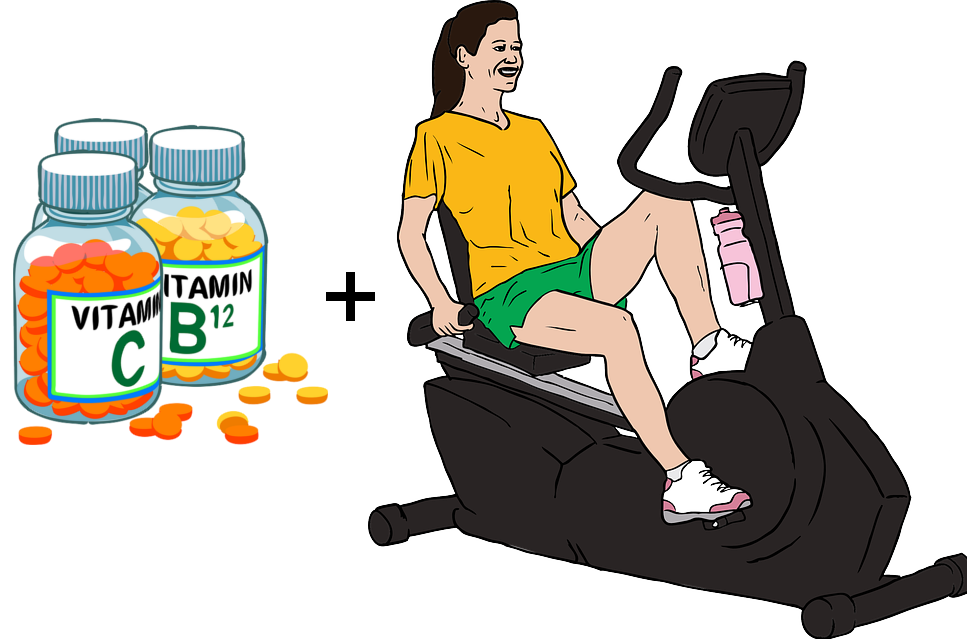
Other than Riluzole, various drugs
can be taken to reduce the severity of symptoms, occupational therapy
can slow down the degeneration of brain cells, physical exercise
strengthens the unaffected muscles and improves the cardiovascular
system, and augmenting your nutritional intake, as ALS patients are
almost always suffer from a deficiency in that area.
 |
|
Fundraising: Recently, an ALS awareness campaign called “The Ice Bucket Challenge” has become viral, with many people participating. A contestant will fill a bucket with ice and water, state who challenged them, and in turn, challenge three others to take part. The contestant then dumps the bucket of ice water on themselves and should then donate US $10 to ALS research. If a contestant refuses the challenge, s/he is expected to donate US $100 instead. By August 25, the campaign managed to raise $79.7 million (compared to $2.5 million in 2013). |
|
Consider donating to ALS research at the ALS Association or the MND Association.
|
mercredi 27 août 2014
What Is ALS?
Inscription à :
Publier les commentaires (Atom)
Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire